If you don’t know how to clear or flush Google Chrome’s DNS cache using chrome://net-internals/#dns then this is the article for you.
Google Chrome has its own DNS cache that improves speed and performance.
This cache is stored for a while and may need to be cleared if the site changes its DNS records.
The browser caches and stores the IP address and all other NS (Name Servers) entries of a website when you visit it.
To do so, you will need to clear or flush Google Chrome’s DNS cache using chrome://net-internals/#dns to access the site.
Before proceeding with these steps, you must save any works in the browser, if any.
How to clear Google Chrome’s DNS cache using chrome://net-internals/#dns
Here’s how to flush Chrome’s DNS cache.
1. Open a blank tab in Chrome and enter the URL mentioned below.
chrome://net-internals/#dns
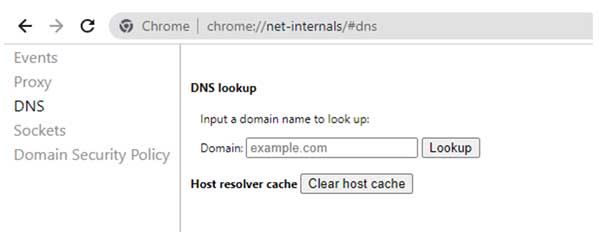
2. Press Enter on the “Clear Host Cache” button.
You have successfully flushed Chrome’s DNS cache.
3. Now type the following URL in a new tab of Chrome then press Enter.
chrome://net-internals/#sockets
4. Select and press Flush Socket Pools.
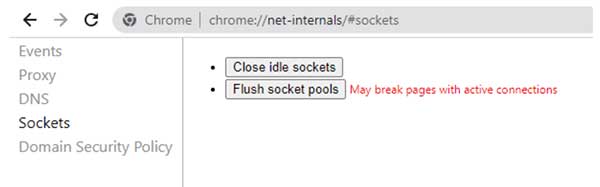
If the message “May break pages with active connections” appears, it means that you need to save all work, if any tab with a logged in account is open, it can be logged out.
5. Close and Restart Chrome.
If clearing the DNS cache in Chrome using the command chrome.//net-internals/dns doesn’t fix the problem, you can try flushing your device’s DNS cache.
Flush DNS cache in Windows 7/8/10/11
Open command prompt as administrator and type ipconfig /flushdns and press enter.
Flush the DNS cache on Linux
Open a terminal and type the following command
$ sudo service network-manager restart
Flush DNS cache on MAC
Open a terminal application on your MAC PC or Macbook and type the following command
$ sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
$ sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Chrome Net Internal DNS?
NetLog, or Net-Internals, is a tool in Chrome that allows users to see DNS cache and other network setup logs in real-time logs, or retrieve NetLog dumps of past data for debugging or troubleshooting by using chrome://net-internals/#dns command.
What is a DNS cache?
DNS cache is cached web page data (name servers, such as a host’s IP address) that helps the browser speed up the browsing process. Incase of issue it should be cleared by using a command chrome://net-internals/#dns in chorme tab.
